What is Diesel Fuel?
Refined from crude oil, diesel fuel is what we call the distillate fuel oil used in some internal combustion engines. Invented by Dr. Rudolf Diesel, the first diesel engines were made in the 1890’s.
In today’s global economy, diesel fuel is used in most heavy equipment applications including tractor trailers, delivery trucks, construction equipment, and buses. Diesel is also used in some pedestrian vehicles such as cars and light trucks.
Diesel-engine generators are used to power remote off-grid sites as well as industrial facilities. These diesel generators are used around the world as a backup emergency power supply for hospitals, government facilities, data centers, and other critical facilities.
How is Diesel Fuel Made?
Diesel oil is refined from crude oil at petroleum refineries. Refineries were first modernized in the 1850’s by Ignacy Luksiewicz, who used the refined products for kerosene lamps, asphalt, oil, and lubricants.
Diesel is made of hydrocarbons that are derived from petroleum. There are three major classes that petroleum crude oils are composed of: paraffinic hydrocarbons, naphthenic hydrocarbons, and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Crude oil can be observed in many forms, depending on the density. Low density oils are thin and light-colored, and are also known as high-gravity crude oils. High density oils are very thick and viscous and appear similar to tar, making them low-gravity crude oils.
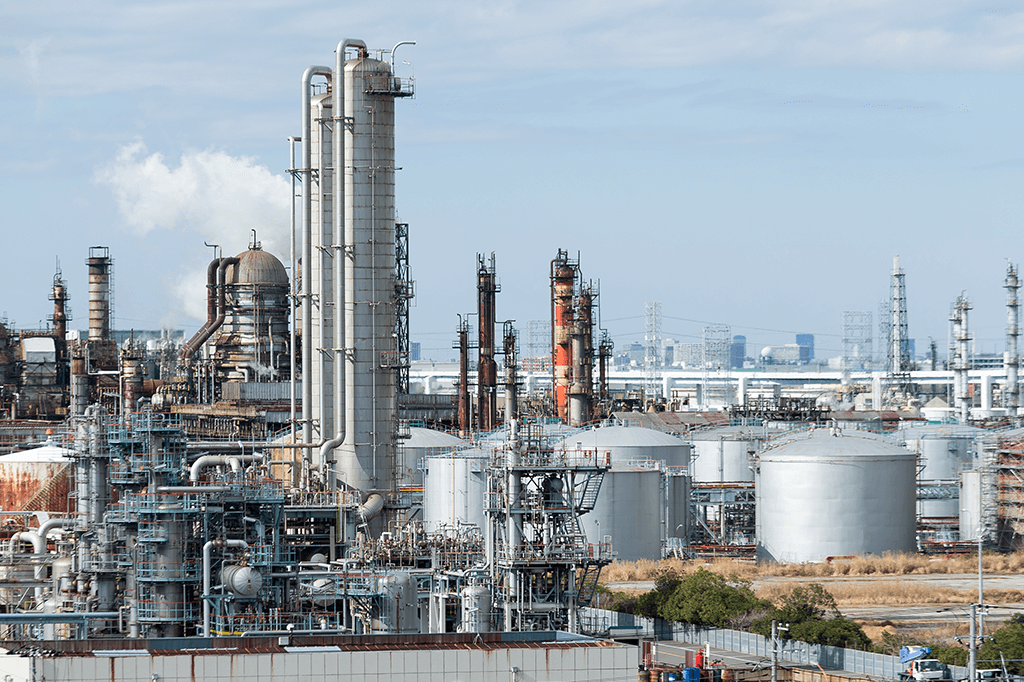

How is Diesel Fuel Refined?
All hydrocarbon-based fuels originate from crude oil which is put through a refinement process called distillation This process will yield various types of fuels ranging from heavy fuel oil to diesel and gasoline.
During the refinement process, crude oil will enter a distillation tower and be boiled to create vapors. These vapors will condense and settle on different trays at different levels. Lighter molecules will settle on higher trays while the heavier ones will reside towards the bottom. The vertical placement of each tray will determine what type of fuel is being collected.
For each 42-Gallon barrel of U.S. crude oil, refineries produce around 11 to 12 gallons of diesel fuel.
Diesel engines are considered to be more fuel-efficient and have more low-end torque than gasoline alternatives. This is why diesel-powered vehicles can go up to 35% farther on a single gallon of fuel when compared to gasoline engines.
What are the Differences Between Diesel Fuels?
Diesel #1
#1 Diesel is often considered a premium fuel, because of its added property benefits. This includes added lubricants that keep engine components from experiencing excessive wear, keeping diesel engines running smoothly for longer periods of time.
Detergents are also added to Diesel #1 before it is delivered to the pump. While the engine is running, the detergents will help clean injectors and other critical fuel system components. This also helps maintain engine power and fuel efficiency.
Diesel #1 has also become the preferred fuel choice as a winter diesel solution because of its low viscosity. This means that the fuel is less likely to gel in extremely cold climates because of the absence of paraffin wax.

Diesel #2
#2 Diesel is also known as “standard” diesel fuel and is commonly available in most refueling stations. Creating #2 diesel does not require as much refinement as #1, making it the less costly of the two. #2 diesel also contains more energy density per gallon of fuel, which means diesel engines will get more power from #2 diesel compared to #1 diesel.

Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel was developed to reduce harmful emissions from diesel powered engines used on public roadways. Starting with the Clean Air Act in 1990, the EPA mandated sulfur content limits to reduce the impacts diesel engine emissions have on public health and the environment. Since December 2010, all highway diesel fuel in the USA has been ULSD.
Off-Road Diesel
Off-road diesel, also known as AG diesel or “red” diesel, has no chemical difference when compared to the #2 diesel you’d typically find at the pump. The difference in off-road diesel is that it has been dyed red to indicate that the fuel was not distributed for on-road use .
Off-road diesel is sold for use in equipment and vehicles that are not operated on public roadways, and are most used to supply fuel to emergency stand-by generators, farm equipment, and construction equipment.

Clear diesel, which is another name for on-road diesels like #1 and #2 is subject to additional taxes because of its on-road use. By dyeing off-road diesel red, it is an easy way to indicate which type of diesel fuel it is under inspection.
Off-road diesel is much cheaper to purchase because it isn’t subject to the same taxes as on-road diesel. Because of this, there are heavy penalties for improperly using off-road diesel.
Biodiesel
Biodiesel has grown in popularity in recent years as the world moves toward green energy solutions.
Biodiesel is recognized as a renewable fuel derived from animal fats and plant oils and is considered a cleaner alternative to #2 diesel made from the petroleum refinement process.
Biodiesel is compatible with almost all modern diesel engines, and there are also bio-blends available (which contain a percentage of petroleum diesel) for other engine applications.
How Does Diesel Compare?
Diesel fuel has been an important contributor of industrial growth around the world. Through utilizing this dynamic energy source, we have developed mass transit systems, backup power solutions, global import/export networks, and more.

Benefits of Using Diesel Fuel
The benefits of utilizing diesel fuel to help shape our world have been countless, however there are a number of advantages and disadvantages that should be mentioned.
Engines powered by diesel fuel are known to get considerably better fuel economy when compared to gasoline engines. Diesel is also much more dense in energy when compared to other petroleum fuels.
Diesel fuels also provide more low-end torque making it much better suited to power heavy equipment such as tractor trailers.
Rising Costs of Diesel Fuel
Unfortunately, diesel fuel also has some disadvantages. For instance, diesel fuel costs have outpaced gasoline over the last year. Compared to last year, on-highway diesel fuel prices have grown by over 35% compared to gasoline which increased by just over 9% during the same period.
In August of 2022, the Bureau of Transportation Statistics reported a staggering rise in diesel costs, with consumer costs increasing 55% from January to June of 2022. This price inflation has slimmed the margins and nearly erases the cost advantage of using diesel in some circumstances.
Contamination in Diesel Fuel
Diesel fuel, especially in bulk storage applications, is also susceptible to microbial contamination which leads to the degradation of fuel.
Diesel fuel contamination can be tricky to resolve, especially if the problem isn’t caught early. If not caught early, diesel fuel contamination can wreak havoc on engines and jeopardizes the operability of critical equipment.

To mitigate diesel fuel contamination issues, it is recommended that diesel fuel be tested often for contamination, as well as be regularly polished to maintain the desired quality of the fuel.
The National Fire Protection Association recognizes the importance of regular fuel quality testing. The NFPA 110 "Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems" requires annual fuel testing to ensure bulk fuel is suitable for long term storage.
There are many ways to test for diesel fuel contamination. Please check out our guide on testing for diesel fuel contamination to learn how to test accurately.




